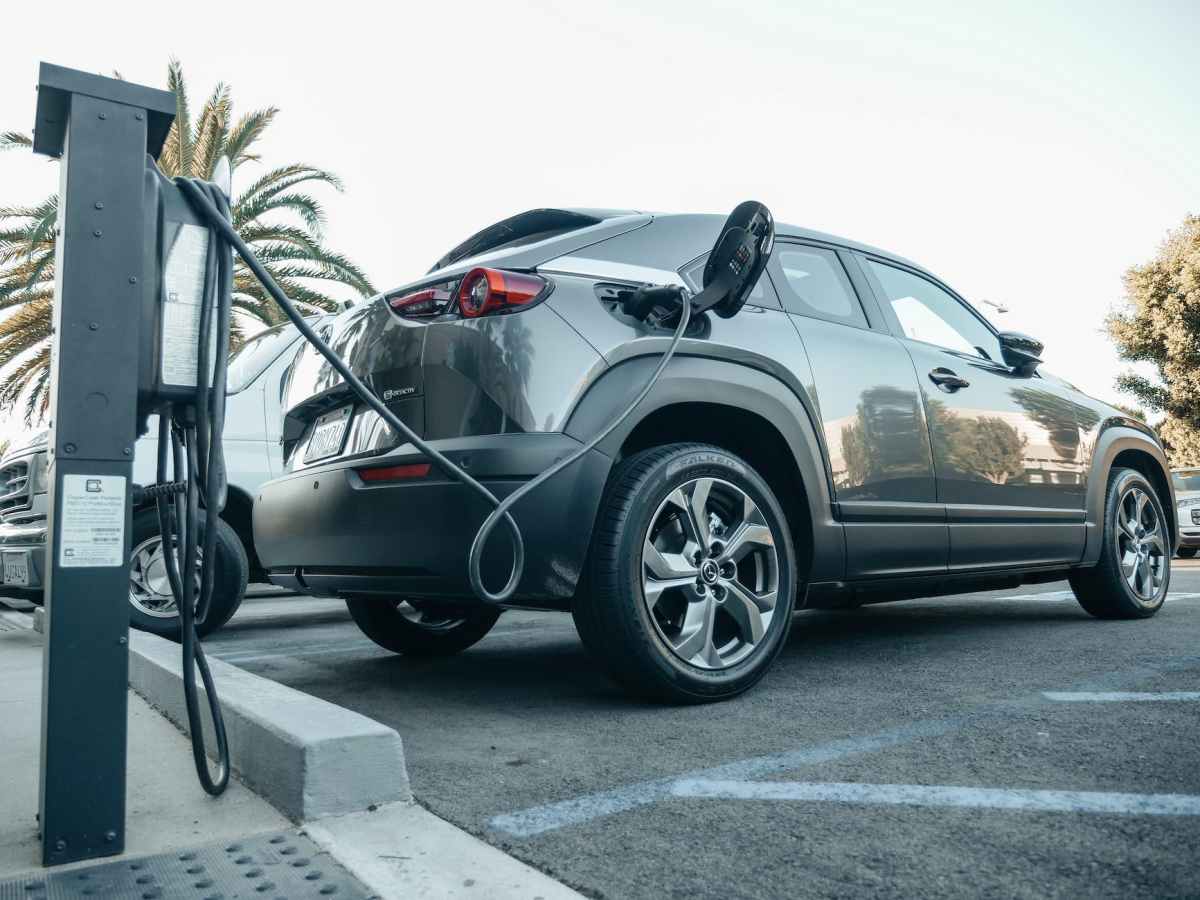
What next? There’s a growing number of Electric Vehicles (EV) on the market. In fact, the diversity of choice doesn’t make choice easy. Such a variety of different sizes and configurations. Cars big and small. Hybrids too. Every new generation offering more range and more bells and whistles (technology).
My car is getting near to its 11th birthday. It runs exceptionally well. Trouble is age, ware and tear, can’t be escaped. Bills start to ramp up as millage takes its toll even if it hasn’t done – yet. German engineering isn’t always what its cracked up to be except my car does fit the stereotype. Temptation is to buy another one.
My first trip to the US was back in the early 1980s. Four of us drove up and down the west coast. Seeing spectacular sights and meeting amazingly friendly people. American cars of that time were of the Cagney & Lacey generation. Meaty metal boxes that handled like a crate of jelly. Gas guzzling but, who cares, gas was cheep in comparison with European prices.
Wide empty roads, outside the cities, where the landscape filled every vista with new wonders. City driving wasn’t so pleasant. Freeways where the occasional Blues Brothers like police car buzzed past at speed. Air quality dropped a million percent (exaggeration). Jams in more lanes than we’d ever imagined possible.
So, are Electric Vehicles (EV) the spawn of the devil? I take the point that not everything is as rosy as the marketing departments of the manufacturers would have us believe. Some prestige models are bulky and heavy. These are not well suited to the narrow pothole heaven of England’s poorly maintained roads.
That said, the change is upon us, and it would seem foolish to go backwards. Once over the initial purchase price, which does seem to be coming down, EVs don’t cost much to run. There’s a simplicity of electric motors which a high-performance reciprocating engine can’t match. Not only that but high-performance reciprocating engines have probably reached the limits of what can be squeezed out of them. Decades of development in reducing tail pipe emissions.
It’s clear Electric Vehicles (EV) have a long way to run. Battery technology will continue to improve. That’s one to bet the house on. It’s because there are so many applications for high power density batteries. If you are aiming at a Nobel Prize in Chemistry, that’s the way to go.
Driving a car with no tail pipe emissions does have a holier than thou feel about it. If we want cities to be healthy places to live, then something must be done. I wouldn’t want to live near the world-famous Hanger Lane Gyratory[1]. Or anything like it. In England we built massive road systems on top of streets designed for the horse and carriage.
Looking at new cars, like the Mercedes-Benz CLA[2], I must admit I’m tempted. Putting that up against the lumbering thundering rust buckets of the 1980s and there’s no comparison whatsoever. Whether it’s sheer performance or climate change that motivate a purchase decision, the days of conventional petrol and diesel cars are numbered.
[1] https://uk-air.defra.gov.uk/networks/site-info?uka_id=EA6&provider=london
[2] https://www.mercedes-benz.co.uk/passengercars/models/saloon/cla-electric/overview.html