Finding aircraft wreckage in the deep ocean is possible. However, it requires a degree of good fortune. Most of all, it requires the searcher to look in the right places. Lots of other factors come into play, particularly if the ocean floor is uneven or mountainous.
The primary tool for imaging the ocean floor is SONAR. That’s using the propagation of sound in water. SONAR can be of two types. One is called “passive” and the other called “active”.
The first case is like using a microphone to listen to what’s going on around. Of course, the device used is named appropriately: a hydrophone. It’s a device tuned to work in water and not air. Afterall, sound travels much faster in a liquid than it does in air.
Passive SONAR depends on the object of interest making a noise. Just like we have directional microphones so we can have directional hydrophones.
Passive SONAR is only useful if the aircraft wreckage is making a noise. Since in the case of Flight MH370, the battery powered underwater location beacons attached to the accident flight recorders have long since stopped working this kind of SONAR isn’t going to be much use.
Active SONAR is analogous to RADAR. That is where a pulse of high frequency sound is sent out through a body of water. Then sensitive hydrophones pick up a reflection of that pulse. It is detected and all sorts of miraculous digital signal processing is done with the acoustic signal, and an image is then formed. From that displayed image the human eye or sophisticated algorithms can make sense of what they are looking at on the sea floor.
Active SONAR can give both range and bearing (direction). Timing the sound pluses from their transmission to reception can give a way of calculating range. Or distance from the object providing a reflection. Bats know how to do this as they navigate the dark.
In sea water, there are complications. Sound does not always travel in a straight line in sea water. The speed of sound in water depends on salinity, temperature and pressure. All three of these factors can be measured and compensated for in the SONAR signal processing that I mentioned above. Helpfully at ocean depths beyond a kilometre the calculations become easier.
The average depth of the Indian Ocean is over 3 kilometres. It’s mountainous underwater too. So, what are the chances of finding flight MH370 on the ocean floor after 10-years[1]? This prospect goes back to my earlier comment. It requires the searcher to look in the right places.
Just imagine encountering the Grand Canyon for the first time. It’s nighttime. An important object is lost in the canyon. You only have the vaguest theories as to where the object has come to rest. With a handheld touch you go out to search. What are the chances of finding the object?
There are several factors that are in your favour. One, you know what the object might look like or, at least, in part. Two, the easy search locations (flat/smooth) may be covered relatively quickly. Three, certain areas of the rocky canyon have already been searched. Still the odds are against finding the lost object without a high degree of good fortune.
I wish the new planned searchers much good future[2].
NOTE 1: one of my student apprentice projects was to design and build a Sing-Around Velocimeter for use in relatively shallow sea water[3]. It worked but was cumbersome in comparison with the simple throw away devices used for temperature depth profiling.
NOTE 2: To get down to the ocean depths required it’s a side-scan sonar that may be used. This active sonar system consists of a towed transducer array that can be set to work at different depths. Imaging objects on the seafloor and underwater terrain is done as a towed array moves slowly forward through the water. The scanning part is the acoustic beam sweeps left and right. Each scan builds up part of an image.
In operation, as the frequency of the sound in water goes up so does the resolution of a potential image but, at the same time, the range of the sonar system goes down. Thus, a sonar system used for surveying may have low and high frequency settings. Unlike sound in air, here high frequency means above 500kHz.
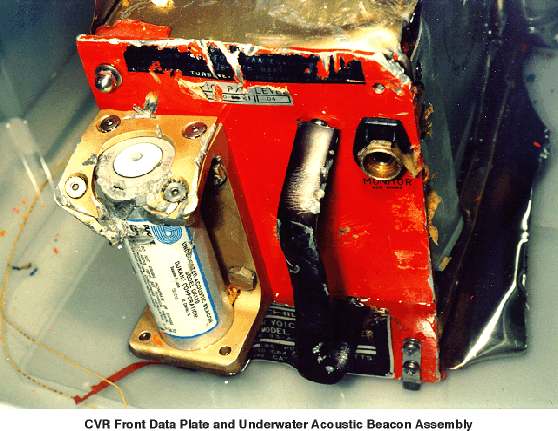
NOTE 3: What will an aircraft accident recorder look like after a decade in the deep ocean? It might have survived well given the nature of the dark cold pressured environment. This picture is of an accident recorder recovered from relatively shallow sea water (Swiss Air Flight 111).
POST: Nice view of what SONAR can do, at least in shallow water Bristol Beaufort wreckage found
[1] https://www.cbsnews.com/news/mh370-plane-malaysia-new-search/