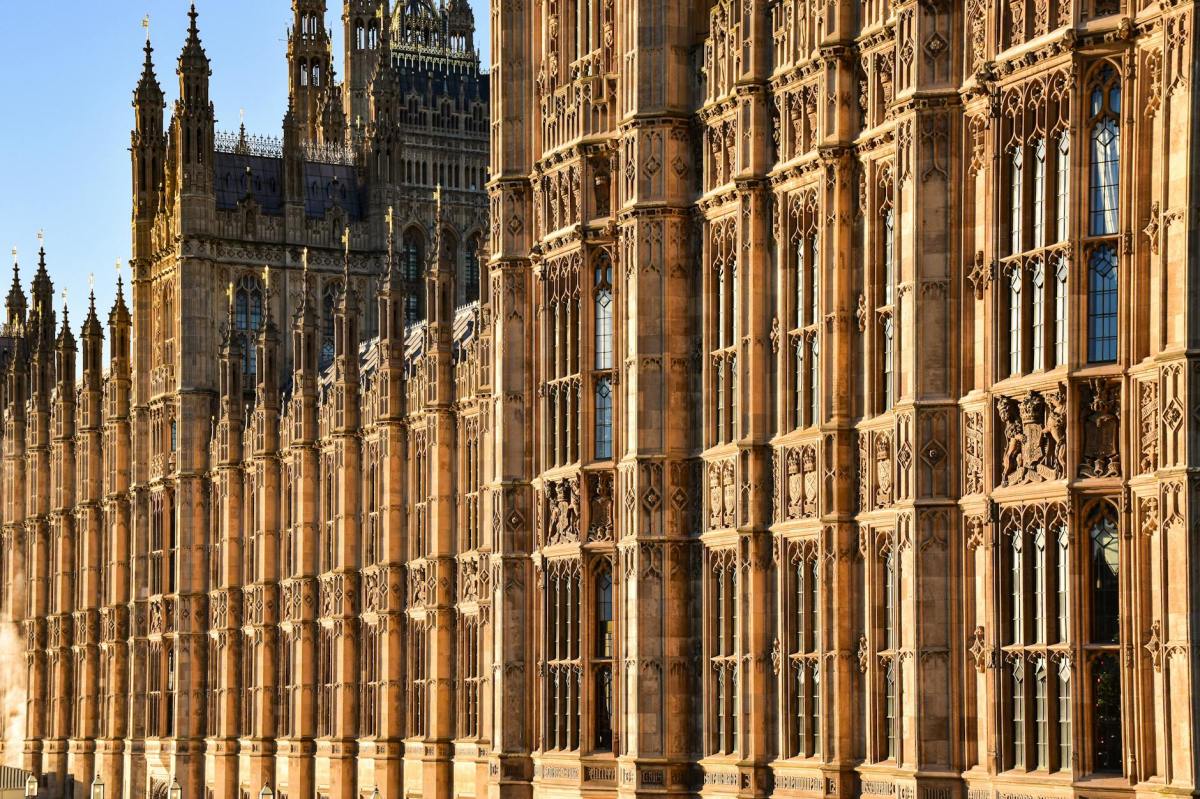
I wouldn’t for one moment propose that the palace of Westminster be demolished. It’s an iconic landmark. No, my point is that the building is entirely ill-suited to be a 21st century parliament building. What served well in the Victorian period now restraints and stultifies its occupants.
Across the great river Thames is another iconic building, London’s Country Hall. That’s no longer an important seat of local government. Throughout the country there are hundreds of former Town Halls, now put to other uses. Lots of listed buildings that are rightly preserved as part of our unique British heritage.
I’m reacting to the News story about the cost of repairs to the Houses of Parliament. Possibly six-decades of work at the cost of tens of billions of pounds. Parliamentarians, who may never see the work finished, will need to decide on different potential courses of action.
Let’s be clear. Six-decades ahead takes us to the year 2086. Those at school now will, they hope, be retired as the final lick of paint is applied. Not only that but who on earth can realistically predict the final cost to the taxpayer of such a never-ending project?
This brings home what real long-term planning is all about. Do we adopt a myopic vision based on sentimentality and stick with the existing palace of Westminster or take a different approach.
Buildings, their structure and form, do shape the way we behave. What would be the point of celebrated architecture if such was irrelevant to the human experience. This has been understood in both Germany and Australia.
British architect Norman Foster’s reconstruction of the Reichstag in Berlin[1], finished in 1999, transformed a 19th-century building into a modern, transparent seat of democracy.
The architecture of Parliament House[2] in Canberra is well worth a tour. To be able to walk over the hill, and on top of the building is a profound statement that suites Australians so well.
My view is that an ambitious nation would look at the next sixty years as an opportunity to forge an identity suited to the future not the past.
So, British Parliamentarians move out of Westminster and look for another solution.
The great River Thames is part of our national story in a way that other rivers are not. The River Severn may be longer, not by a lot, but it doesn’t have the navigation that made the Thames and the city of London so pivotal in our national story. What other locations on the River Thames would fit the bill? Likely more central but remaining well connected. My suggestion might shock some people and create an instant rejection.
Our national story is one of roads, rivers, canals and railways. Moving inland along the path of the River Thames, a fast efficient railway service leads to a large town, not yet a city. The ruins of Reading Abbey, founded by King Henry I in 1121 “for the salvation of my soul,” reminds me that a sense of continuity has its place. That’s apt. For the salvation of the souls of our elected representatives, why not choose Reading.
I’m not saying the famous Reading Gaol[3] could be repurposed. Anyway, it’s been sold. But there are numerous sites in that town where a new parliament building would shine a beacon of hope.
[1] https://www.fosterandpartners.com/projects/reichstag-new-german-parliament
[2] https://www.aph.gov.au/Visit_Parliament
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/The_Ballad_of_Reading_Gaol